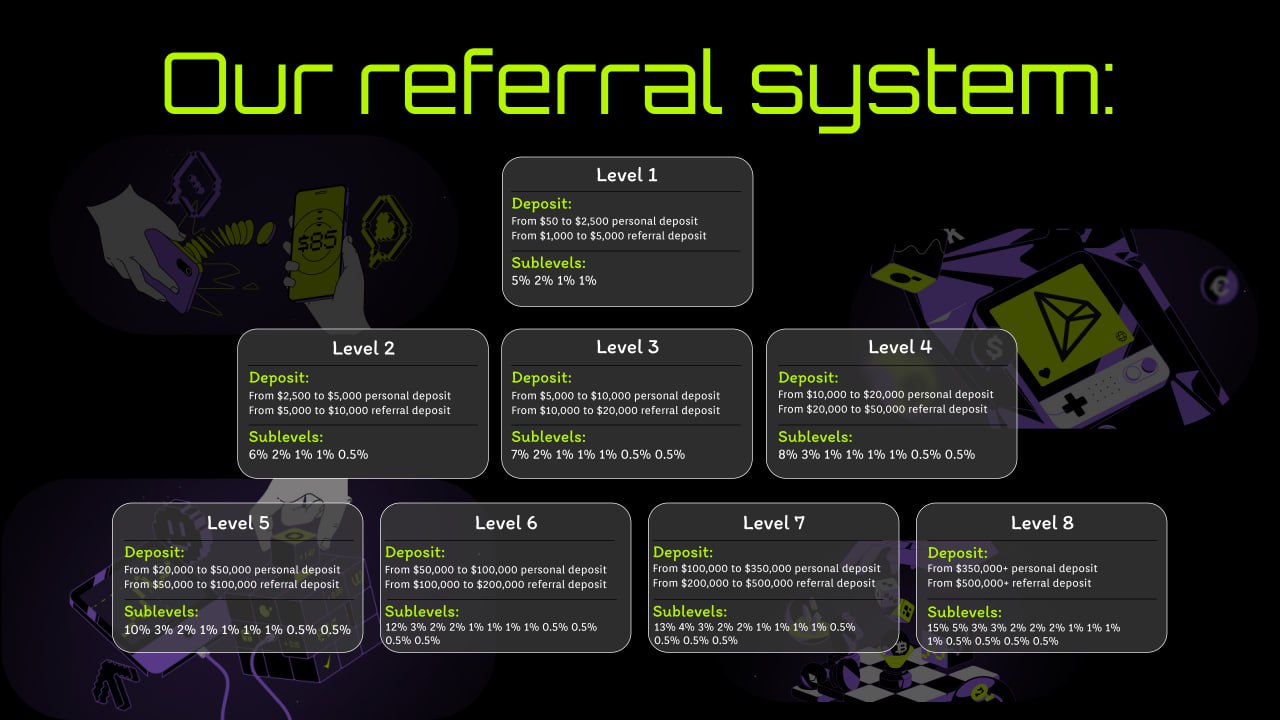
What is cryptocurrency staking?
Cryptocurrency staking is the process of participating in transaction validation and maintaining blockchain security in a network that uses the Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism or its variations (for example, Delegated Proof of Stake, DPoS). In return, participants receive rewards in the form of new tokens or transaction fees.
Learn more about staking
Key aspects of staking:

Proof of Stake (PoS)
Unlike Proof of Work (PoW), where miners solve complex mathematical problems, in PoS validators create new blocks and confirm transactions based on the amount of cryptocurrency they “lock” or “stake” in the network.

Funds Locking
To participate in staking, a user must hold a certain amount of cryptocurrency in their wallet, which will be locked for a specific period. This serves as a guarantee of honest behavior, since improper actions may lead to the loss of part or all of the staked funds (slashing mechanism).

Rewards
Staking participants receive rewards in the form of new coins or transaction fees, proportional to the amount and duration of their stake. The reward may vary depending on the network and conditions.

Delegation
In some networks (for example, Cosmos, Tezos), users can delegate their tokens to a validator who will validate transactions on their behalf. Delegators receive a share of the reward earned by the validator.

Simplicity and Accessibility
Staking requires fewer computing resources compared to mining, which makes it more accessible for regular users. Many exchanges and wallets offer staking services, making participation easier.
Advantages of Staking

Energy Efficiency
PoS requires significantly less energy compared to PoW, making it more environmentally sustainable.
Network Support
Participation in staking helps maintain the security and decentralization of the blockchain.
Passive Income
Users can earn additional tokens simply by holding their cryptocurrencies in staking.
Examples of cryptocurrencies that support staking
Ethereum 2.0
Ethereum is transitioning from PoW to PoS, allowing users to stake their ETH to participate in the network.

Polkadot (DOT)
Uses Nominated Proof of Stake (NPoS), where users can nominate validators.

Cardano (ADA)
Supports staking through delegation and validator pools.

Tezos (XTZ)
Allows users to delegate their XTZ to validators (bakers) to participate in staking.
Staking process

1. Choosing a cryptocurrency
The user selects a cryptocurrency that supports staking.
2. Creating or selecting a wallet
The user creates a wallet that supports staking or uses an exchange offering this service.
3. Locking funds
The user locks (stakes) their tokens in the network or delegates them to a validator.
4. Receiving rewards
For participating in the network, the user receives rewards, which can be automatically reinvested or withdrawn.
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more
Learn more